All That You Need to Know
Breast surgery encompasses several surgical and non-surgical techniques aimed at enlargement, reconstruction, and reduction of the breasts. These can be performed to meet aesthetic, reconstructive, and physical comfort needs and concerns, such as cosmetic augmentation, mastectomy reconstruction, and relief from discomfort caused by large breasts. This detailed manual covers the types of breast procedures and their intended uses, methodologies, risks, and paths to recovery and the cost involved.

Breast Augmentation

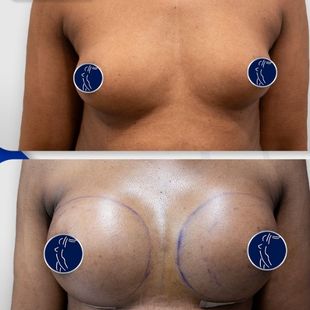
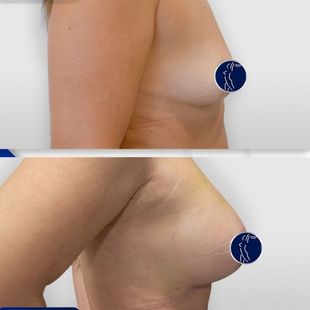
Augmentation mammoplasty, more commonly referred to as breast augmentation surgery, is among those top cosmetic surgeries that are in high demand all over the world. The surgery aims at enhancing the size, shape, and fullness of the breasts with implants or fat transfer. The following detailed guide will provide information on everything one needs to know about breast augmentation: reasons for surgery, types of implants, the surgical process, recovery, risks, and costs.
4250 £
Breast Aesthetics
Techniques
1. Saline Implants
- Composition: Filled with salt water that is sterile.
- Advantages: Should the implant shell leak, the saline will be absorbed and naturally expelled by the body.
- Feel: Generally, silicone implants feel softer and more like natural breast tissue.
- Insertion: Can be inserted empty and filled once in place, allowing for smaller incisions.
2. Silicone Implants
- Composition: Filled with silicone gel.
- Advantages: Feels softer and more natural compared to other types of breast implants.
- Insertion: Pre-filled and thus requires a slightly larger incision.
3. Gummy Bear Implants
- Composition: A type of silicone implant that has a thicker, more cohesive gel.
- Advantages: Keeps its shape even if the shell is ruptured.
- Feel: Also tends to be firmer and less likely to wrinkle or fold.
4. Fat Transfer
- Process: Fat is taken from other areas of the body (like the abdomen and thighs) via liposuction, cleaned, and then injected into the breasts.
- Advantages: Makes use of the body's tissue, bypassing synthetic implants. •
- Limitations: It offers a more subtle increase in breast size, and one may need multiple sessions to obtain desired results.
Surgical Process
1. Consultation
- Discussion: Goals, expectations and health history.
- Examination: Physical examination and measurements of the breasts.
- Planning: Decision on implant type, size, incision location and placement.
You can have an initial pre-examination with your Wellcome Healthy Life Consultant.
2. Pre-Operative Preparation
- Instructions: Guidelines on eating, drinking, and medications.
- Tests: Blood tests and medical evaluations as needed.
3. Anesthesia
- Type: General anesthesia is commonly used, where the patient sleeps and remains insensitive to pain during the procedure.
4. Incision Options
- Inframammary: A sub-breast incision performed in the fold of the breast where ample access allows accurate insertion of the implant.
- Periareolar: Incision around the bottom edge of the areola, which allows for least possibilities to show scars.
- Transaxillary: Armpit incision, by which no scarring on the breast itself is obtained.
- Transumbilical (TUBA): Through the navel, this is less common and is applied in a few cases for saline implants.
5. Implant Placement
- Submuscular (Under the Muscle): The implant would be placed under the pectoral muscle. Advantages include a more natural appearance and a decreased risk of capsular contracture.
- Subglandular (Above the Muscle): The implant is placed directly behind the breast tissue. Recovery may be faster, but it increases visible rippling and capsular contracture.
6. Closing Incisions
- Methods: The incisions are closed by sutures or skin adhesives or surgical tape.
7. Post-Operative Care
- Dressings: The patient is dressed with bandages and a support bra to reduce swelling and support the breasts.
- Instructions: Specific care and medication to apply or take orally; follow-up appointments.
Breast Lift (Mastopexy)

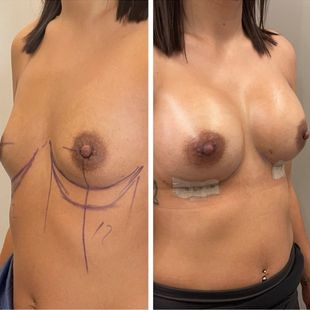
A mastopexy is the surgical elevation and firming of the breasts by removal of extra skin and tightening the structures surrounding the breasts. It reshapes the contour of the breast, thereby correcting sagging and giving a more youthful and attractive look. The following is a detailed explanation of breast lift surgery, from motives for conducting it to the various techniques, recovery, risks involved, and cost.
Procedure
1. Consultation
- Discussion: Goals, expectations, and medical history.
- Examination: Physical examination and measurements of the breasts.
- Planning: Decision on the appropriate surgical technique and incision type.
2. Pre-Operative Preparation
- Instructions: Guidelines regarding eating and drinking, medications, and quitting smoking
- Tests: Blood tests and medical check-ups where necessary
3. Anesthesia
- Type: General anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation to ensure comfort during the procedure is maintained
4. Incision and Reshaping
- Incision: According to the selected technique.
- Reshaping: Elevate underlying breast tissue and reshape; remove extra skin and reposition nipple and areola higher on the breast.
- Closure: Stitch the incisions with sutures, skin adhesive, or surgical tape.
5. Post-Operative Care
- Dressings: Bandages and a support bra to reduce swelling and support breasts.
- Instructions: Special home care, ointments or medications to apply or take orally, and follow-up appointments.You have the opportunity to undergo an initial online pre examination with your consultant / doctor through the Wellcome Online Health Center
Contact Consultant/Doctor Totally Free!
Recovery
Initial Recovery Period:
- 24 to 48 hours rest with restricted mobility.
- Pain, swelling, and bruising are common; these are managed by medications.
First Week:
- One can resume light activities, though strenuous activity should be avoided.
- Follow-up visit to the surgeon for follow-up on healing.
Weeks 2-4:
- Gradual resumption of normal activities.
- Avoid lifting heavy things and doing strenuous exercises
Long-Term:
- The complete recovery and hence the final result may take a few months.
- Scars fade over time but may never completely disappear.
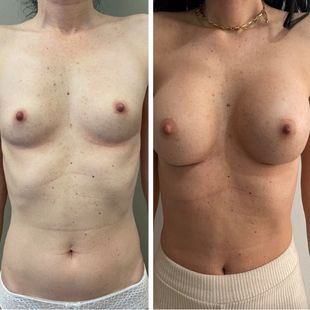
Breast Reduction
Purpose
The purpose of the reduction mammoplasty or breast reduction surgery is to reduce the size of the breasts to alleviate discomfort such as back pain, neck pain, and skin irritation, with the aim of achieving a size of the breasts that is in proportion to the body.
Techniques
- Anchor Incision: Incisions are made around the areola, vertically down to the breast crease, and horizontally along the crease.
- Vertical Incision: Incisions are made around the areola and vertically down, without making the horizontal incision.
- Liposuction: In cases involving minor reductions with minimal sagging, small incisions are made through which the liposuction cannula can be inserted.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia.
- Incision: Depending upon the technique.
- Tissue Removal: The excessive breast tissue, fat, and skin are excised.
- Reshaping: Reshaping the remaining breast tissue and repositioning of the nipple and areola is performed.
- Closure: Incisions closed with sutures, skin adhesive, or surgical tape.
Recovery
- Initial recovery usually takes about one week.
- A couple of weeks of low activity
- A couple of months with some swelling and tenderness
- Follow-up care to check on the healing process
Breast Reconstruction
Purpose
Rebuilding the shape and appearance of a breast, most commonly after mastectomy or lumpectomy due to breast cancer and other illnesses.
Techniques
- Implant-Based Reconstruction: This uses saline or silicone implants.
- Autologous Reconstruction (Flap Procedures): Utilizes the patient's own tissue from another part of the body like from the abdomen, back, or buttocks.
- TRAM Flap: Tissue from the lower abdomen.
- DIEP Flap: Tissue from the abdomen, preserving abdominal muscles.
- Latissimus Dorsi Flap: Tissue from the upper back.
- Combination: Uses both implants and tissue flaps.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia.
- Implant-Based:
- Tissue Expander: A temporary device is placed to expand the tissue.
- Implant Placement: The permanent implant is placed inside after expansion.
- Flap-Based:
- Tissue moved from donor site to chest
- Microsurgery reconnects the blood vessels
- Closure: Incisions stitched shut.
Recovery
- Initial hospital stay of a few days.
- Recovery that may take weeks or up to several months
- Follow-up usually needed for addressing additional procedures/adjustments.
Non-Surgical Breast Procedures
Purpose
Non-surgical options aim to enhance the appearance of the breasts without invasive surgery. These include treatments for firmness, lifting, and minor augmentation.
Techniques
- Dermal Fillers: Hyaluronic acid-based fillers are injected to add volume and contour.
- Botox Injections: Used to achieve a minor lift by relaxing muscles that pull the breasts downward.
- Laser Treatments: Stimulate collagen production to improve skin elasticity and firmness.
- Radiofrequency Therapy: Uses radiofrequency energy to tighten skin and enhance the breast shape.
Procedure
- Consultation: Assessment of suitability and desired outcomes.
- Treatment: Performed in an outpatient setting.
- Duration: Sessions typically last 30 minutes to an hour.
Recovery
- Minimal downtime.
- Immediate return to normal activities.
- Results may vary and require maintenance treatments.
Conclusion
Cosmetic enhancement, reconstruction, or relief from discomfort are various options available with breast procedures. Each of the procedures has its techniques, risks, recovery processes, and costs. Consulting a qualified plastic surgeon will help not only in discussing individual goals and expectations but will also help in choosing the most suitable procedure. Desire for an outcome and consultation with professionals will go a long way in helping one decide and create an enhancement in the overall well-being.
Recovery Time
-
Initial Recovery Period- 24 to 48 hours of complete rest with minimal mobilization.
- Pain, swelling, and ecchymosis are common features and medications are provided. -
First Week- Gentle activities can be resumed; however, strenuous actions should be avoided.
- Follow-up visit with the operating surgeon for the review of the ongoing healing process. -
Weeks 2-6- Gradual resumption of activities.
- Avoid lifting heavy weights and highly strenuous activities. -
Long-Term- The healing and the final result of the surgical procedure may take several months.
- Scars will fade over time but may never completely disappear.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who is a good candidate for breast augmentation?
What are the different types of breast implants?
Where will the surgeon place the incisions?
How is a breast lift different from breast augmentation?
Will a breast lift & breast augmentation affect my ability to breastfeed?
Average costs around the world
-
Türkiye
3,000.00 € -
Mexico
3,500.00 € -
Thailand
4,000.00 € -
United States
7,000.00 € -
United Kingdom
6,000.00 € -
Australia
6,000.00 €
-
Get Quality Treatments You can get an idea of the quality of the clinics & hospitals by reading verified customer reviews of their previous experience to make your decision with confidence
-
Gain Time Don't waste time checking recommendations from friends and other websites. Collect offers for your needs online and save time that you could spend with your loved ones.
-
Best-Matched Offers Get personalized offers by answering a few specific questions about your treatment needs. Quickly receive the best-matched offers from over 100 clinics and hospitals
-
Be Protected At every step of your journey, Wellcome preserves your experience. We'll have your back so you can get on with your work in peace.