Cataract
6 results foundCataract: Understanding, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Cataracts are one of the most common vision problems, especially among older adults. This condition is related to a cloudychange of the normally clear lens inside the eye that allows light to pass through and be focused on the retina. Cataracts cloud vision and, if left untreated, can seriously impair vision. Fortunately, cataracts are treatable, and with proper care, most individuals are able to regain clear vision. In this article, we’ll explore what cataracts are, their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
What Are Cataracts?
A cataract is a condition where the natural lens of the eye, located behind the iris and pupil, becomes cloudy. This lens is responsible for focusing light onto the retina, which allows for clear vision. As the lens becomes cloudy, it blocks or distorts the light, leading to blurred or hazy vision. Cataracts often progress slowly, and many individuals may not notice changes in vision at first. Over time, though, this clouding worsens, and vision can be severely affected.
Both eyes can be involved, though one may be far worse than the other because cataracts usually do not grow at exactly the same time. The common cause of cataract formation involves aging, although they can also result from an injury, certain medicines, or diseases affecting health. Symptoms include
Symptoms of Cataracts
The majority of the time, cataracts form very slowly, sometimes barely perceptible. The most common symptoms of cataracts include
Blurry or Cloudy Vision: It usually starts with gradual blurring or clouding of vision. The colors may not appear as bright, and the vision might get foggy or hazy.
Impaired Night Vision: As cataracts worsen, they can limit a person's ability to see well at night or in low light. For example, driving at night may be more difficult due to glare from headlights and streetlights.
Increased Sensitivity to Light and Glare: Individuals suffering from cataracts develop increased sensitivity to bright light. This makes one feel uncomfortable in the sun or artificial lighting.
Partial vision in one eye may lead to double vision where a person sees two images instead of one.
Frequent changes in the prescription of eyeglasses may be experienced by persons with cataracts, as this condition impacts the way light focuses on the retina.
If you notice any of these symptoms, make a visit for an eye checkup to rule out cataract problems through an optometrist or ophthalmologist.
Causes and Risk Factors
Cataract formation is strongly related to the natural process of aging. However, there are a number of factors that can enhance the chance of a person developing cataracts:
Age: Most instances of cataract indeed involve age-related factors, as many people over 60 have some degree of development. As people get older, the risk increases.
Genetics: Cataract development may be based on family history. In this regard, if a close relative has had cataracts, then the tendency of developing it could be higher.
Diabetes: Those suffering from diabetes are at higher risk for developing cataracts due to high blood sugar levels resulting in changes to the lens of the eye.
Smoking: It accelerates the development of cataract because of increased oxidative stress in the eye. Smokers have more risk than nonsmokers.
Sun Exposure: People with long exposure to UV radiation of sunlight may increase the chances of developing cataract. It is highly advisable to wear sunglasses that block out UV light in order to protect your eyes from damage.
Eye Injury or Surgery: Past trauma or surgery involving the eyes may make a cataract more likely to form in that eye.
Medication Use: Prolonged use of certain drugs like corticosteroids is one of the risk factors for developing cataracts.
Cataract Diagnosis
A cataract diagnosis requires a comprehensive eye exam by an eye care professional; it may involve:
Visual Acuity Test: This test will measure your clarity of vision at different distances. This test is essential in determining the level of your loss of vision caused by the cataract.
Slit-Lamp Examination: A slit lamp is a microscope that may be used by the doctor to take a closer look at the front and back of the eye. This, in turn, helps the doctor to see the cloudiness of the lens better and also the extent of cataract formation.
Retinal Exam: The doctor will dilate your pupils to examine the retina and optic nerve to watch for other conditions that may be affecting your vision.
Tonometry: This test gauges the pressure inside the eye, which can help rule out almost any instances of glaucoma, which often accompanies cataracts.
Treatment Options for Cataracts
Treatment options for cataract vary. For early stages, some changes in lifestyle or vision correction may be enough to cope with its symptoms. However, when the cataracts are in advanced stages and significantly impairing the patient's vision, surgery is usually the best option.
Eyeglasses or Contact Lenses: In early cataract development, an optometrist might be able to help improve your sight through a new eyeglass prescription or brighter lighting.
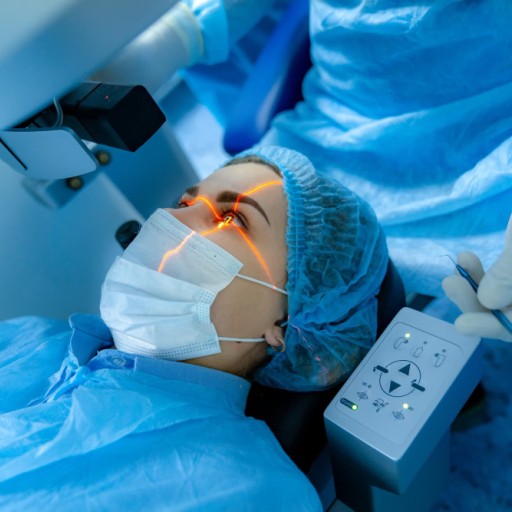
Cataract Surgery: The most effective mode of treatment for cataracts is through cataract surgery. In the course of surgery, the cloudy lens is replaced with an artificial intraocular lens. Generally speaking, it is a safe and effective type of surgery. Most people undergoing this surgery have a much-improved vision.
Laser Surgery: There are chances that laser technology may be used during the course of cataract surgery to fragment the cloudy lens in order to remove it effortlessly.
In general, cataract surgery is done on an outpatient basis, and most individuals recover within a few days. The healing process may involve the use of eye drops according to prescription and the use of an eye shield when sleeping during the initial period.
Prevention of Cataracts
Although a number of risk factors are unavoidable, such as age and genetics, there are several ways one can reduce their risks of developing cataracts:
Wear Shades: Keep your eyes shielded from damaging UV rays with sunglasses that block 100% of the UVA and UVB light.
Quit Smoking: Where smoking is concerned, it reduces the chances of developing cataracts and also keeps your eyes generally healthy.
Control Diabetes: People with diabetes will reduce their chances of developing cataracts, among other complications within the eyes, by managing their blood sugar levels.
Eat a balanced diet: A diet high in antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, may help protect your eyes against oxidative damage and reduce your risk of cataracts. Foods rich in these vitamins include leafy greens, berries, and nuts.
Regular eye examination: Regular visits to the eye care professional may help detect cataracts early and monitor eye health over time.
Cataract Surgery: What to Expect
Cataract surgery is a quick and highly effective procedure that can often restore clear vision. The surgery is usually performed on an outpatient basis, and you will return home the same day. Here's what you can expect:
Preparation: You may be given eye drops to numb the area and relax you before the surgery. You will also be asked to remove contact lenses and any makeup.
Surgery: This involves the surgeon making a small incision in the eye, through which the cloudy lens is taken out. An artificial intraocular lens (IOL) then replaces the natural lens.
Recovery: Most individuals do not experience significant discomfort after the surgery.Eye drops can be prescribed for preventing infection and further inflammation. Improvements to vision usually begin within a few days.
Outlook and Long-Term Care
Cataract surgery is quite successful, and the majority of the patients enjoy improved vision considerably afterward. Nevertheless, it will be relevant to continue regular eye check-ups to monitor other probable eye conditions such as glaucoma or macular degeneration. By maintaining eye health with a balanced lifestyle and protective measures, an individual can preserve their vision for a longer period.
Conclusion
Cataracts are one of the most common eye conditions that cause blurry or cloudy vision. They can easily be treated with early detection. Really effective treatment is cataract surgery, which restores eyesight for so many people. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can be a valuable resource for you to take proactive steps in protecting your eye health and enjoying years of clearer vision.