Mole Removal
2 results foundMole Removal: Safe and Effective Solutions for Skin Health and Aesthetic Concerns
Moles are common skin growths that can come in a variety of sizes, colors, and shapes. Although most moles are benign and non-threatening, many people opt to remove them for cosmetic purposes or due to perceived health risks. Mole removal is one of the most popular cosmetic and medical treatments to help individuals facilitate better skin or a mole that shows signs of change or suspicion. In this article, we will discuss the methods of mole removal, when it is advisable to resort to the procedure, and what to expect during and after treatment.
What is Mole Removal?
Mole removal is a cosmetic or medical procedure to eliminate moles, also called nevi, from the skin. Moles are clusters of pigmented cells that can occur anywhere in the body. Though usually harmless, moles can sometimes be uncomfortable, grow in areas where they continuously get irritated, or change in appearance over time and thus raise concerns. Mole removal can be done for cosmetic reasons, to avoid irritation, or for medical purposes when a mole shows potential skin cancer (melanoma).
This procedure can be done in various ways, and the technique to be used will depend on the size, location, and type of mole to be removed.
Why Should Moles Be Removed?
There could be several reasons why one would want to remove a mole:
Aesthetic Concernations: Many people resort to mole removal to enhance their skin appearance. Moles can make some individuals conscious, especially if they are big, raised, or even located at strategic places on the body; therefore, the reasons for removing them might be cosmetic.
Irritation or Discomfort: Moles that constantly rub against your clothes or are frequently injured by shaving, for instance, may get irritated and uncomfortable. Such could be prevented from causing discomfort or possible infection by removal.
Health Issues: A mole that changes in size, shape, color, or one that bleeds or itches may be the development of melanoma, a type of skin cancer. All such moles must be evaluated by your doctor and may be surgically removed as a precautionary or diagnostic measure.
Preventive Measures: In cases where a mole has a history of being suspicious or problematic, regular removal helps monitor changes to avoid the risk of development into cancer.
When Should You Remove a Mole?
You should consider mole removal if:
The mole becomes painful, itchy, or starts to bleed.
It changes in color, size, or shape, which could indicate skin cancer.
The mole is in an area where it is continuously irritated, such as the neck, face, or underarms. The mole is large, unsightly, or you just feel uncomfortable with its appearance. Before removing a mole, it is always advisable to consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional. They can assess whether the mole is benign or if it needs further examination to eliminate any potential health risks.
Various Methods of Mole Removal
There are various methods of mole removal, each with its own advantages and suitable indications. The technique used depends on such factors as the size, nature, and location of the mole and the possibility of skin cancer.
Excision with Sutures: This is usually for larger or deeper moles. The mole is surgically removed using a scalpel, and stitches are put in. This method ensures that the entire mole, including the roots, is removed.
Shaving Removal: The shaving removal is usually used in the case of raised moles. This process involves shaving off the mole from the skin level with a surgical blade carefully. It doesn't require stitches, but the deeper moles might not get fully treated with this method.
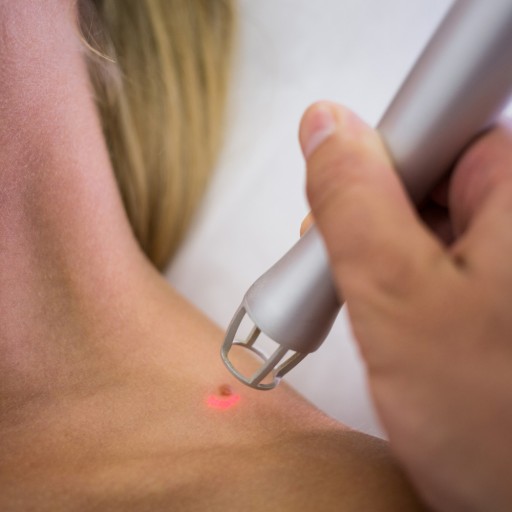
Laser Removal: This procedure involves the use of a laser that breaks down the pigment within the mole. This approach is less commonly used for larger moles but is effective for smaller, flat moles or for cosmetic purposes. It generally requires no stitches and has minimal scarring.
Cryotherapy (Freezing): Cryotherapy involves freezing the mole with liquid nitrogen. This method is effective for small, benign moles but may not be appropriate for deeper or suspicious moles. The mole will fall off as the skin heals.
Electrosurgery: This involves the use of high-frequency electrical currents to remove a mole. It is effective for small, raised moles and helps prevent bleeding during the procedure. This is usually followed by a healing process that may involve a small scab forming.
The Mole Removal Procedure: What to Expect
Mole removal is usually done at the dermatologist's office or a medical clinic and often under local anesthesia. Here's a general idea of what you might expect during the procedure:
Consultation: This is the initial step that regards seeing a healthcare professional. They will inspect the mole and ask questions regarding one's history and symptoms. If the mole looks suspicious, then a biopsy might be considered to test for cancer before removing it.
Preparation: The area around the mole is cleaned, and a local anesthetic is given by injection to numb the area. In this way, you will not feel any pain during the procedure.
Removal: The mole is removed by one of the methods above, depending on its type, size, and location.
Aftercare: After the mole is removed, you’ll be given instructions for proper aftercare, which may include cleaning the area, applying ointment, and avoiding direct sun exposure. If stitches are used, you’ll need to return for a follow-up appointment to have them removed.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery after mole removal is usually rapid and relatively painless, but there are a few important aftercare steps to ensure proper healing and avoid complications:
Keep the Area Clean: Gently clean the area with mild soap and water to prevent infection.
Apply Ointment: You may be instructed to apply a topical antibiotic ointment to prevent infection and promote healing.
Avoid Scratching or Picking at Scabs: Avoid touching or picking at the site of removal for any reason, to avoid scarring or infection.
Infection: Be aware of possible signs and symptoms of infection, such as redness, swelling, or drainage. If these occur, call your healthcare provider right away.
Follow-Up: If sutures were used, a follow-up visit will be required in 7 to 10 days after the procedure to remove the sutures.
Risks and Complications of Mole Removal
Even though generally safe, mole removal has associated risks and complications:
Scarring: Though the degree varies with the type of method, there may be a little scarring. Excision with stitches usually results in a small scar, although it normally fades with time.
Infection: Infection, though rare, can occur from any surgical procedure, but its possibility is greatly reduced with good follow-up care.
Recurrence: If the mole wasn't completely removed, then some may recur in the very same area.
Changes in Skin Texture or Pigmentation: A fair number of people may have skin textural changes or pigmentation following the site of removal, although most usually improve with time.
Mole Removal Cost
The cost of mole removal varies depending on factors such as the location of the mole, the method of removal, and whether it is done for cosmetic or medical reasons. On average, the cost can range from $150 to $1,000 or more per mole. If the removal is deemed medically necessary, insurance may cover some of the cost, but this depends on your specific insurance plan.
Conclusion
Mole removal is a safe, effective way to address unwanted or suspicious moles. Whether for cosmetic purposes or health concerns, there are various methods available to suit individual needs. With proper consultation, careful procedure selection, and good aftercare, you can enjoy smooth, clear skin with minimal risk of complications. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for mole removal and to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the procedure.