Quote of Este Center
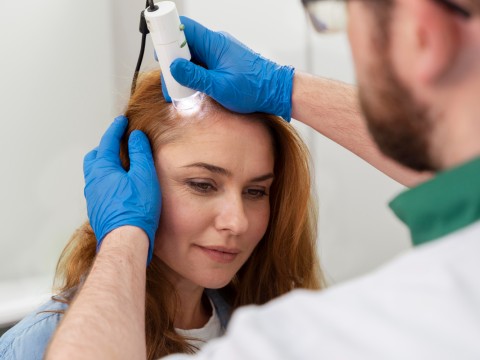
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) is a modern technique used for hair transplantation. In this method, individual hair follicles are extracted (typically from the back of the scalp) and transplanted to the recipient area. FUE is preferred for its less invasive nature and minimal scarring. The recovery process is generally quick, and it provides a natural appearance to the transplanted hair.
- Health Insurance
-
Accommodation
- Online Healthy Life Assistant 9/5
- Post - Experience Follow Up 6 Month
-
Extra Privileges
- Transfer

- Health Insurance
-
Accommodation
- Online Healthy Life Assistant 24/7
- Post - Experience Follow Up 1 Year
- Pre-Treatment Doctor Consultation
-
Extra Privileges
- Transfer

 Private
Private
- Health Insurance
- Healthy Life Butler
- Post - Experience Follow Up 2 Year
- World-Famous Doctor Consultation
-
Extra Privileges
No suitable hotel found for the relevant dates!
* Price varies depending on extra and upgrade selections.
-
Hair TransplantSelectStarting From 2,200.00 €
Follow Your Doctor's Instructions: Your doctor will provide specific instructions tailored to your lifestyle and medications. It is essential to follow these instructions closely.
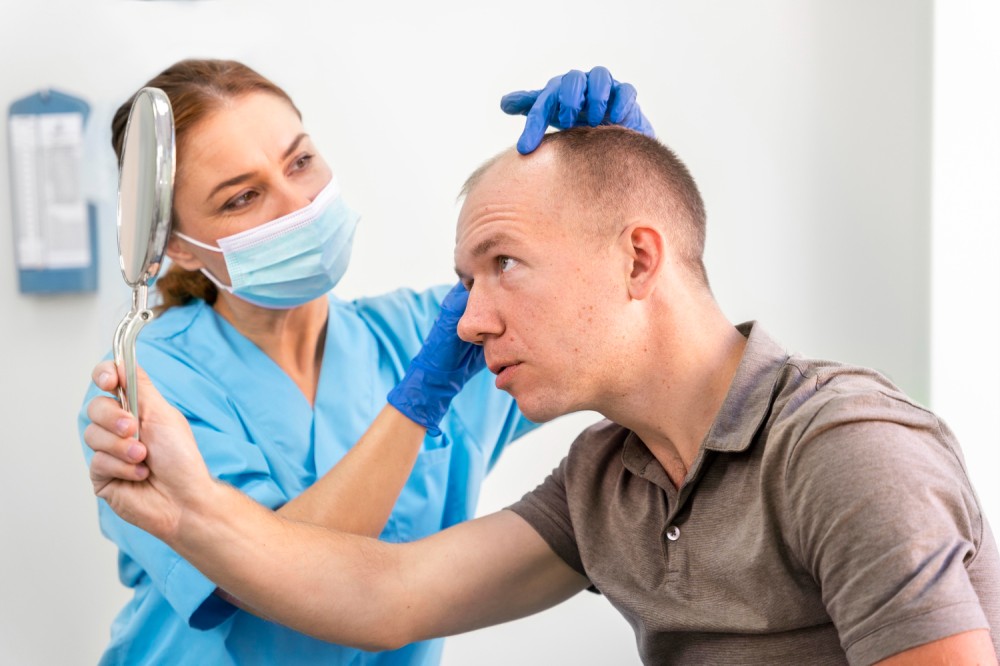
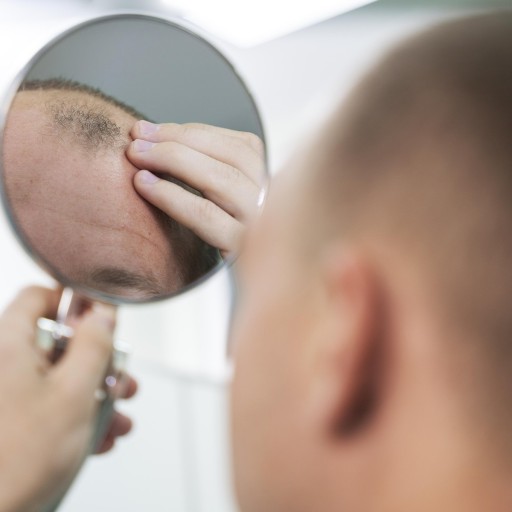
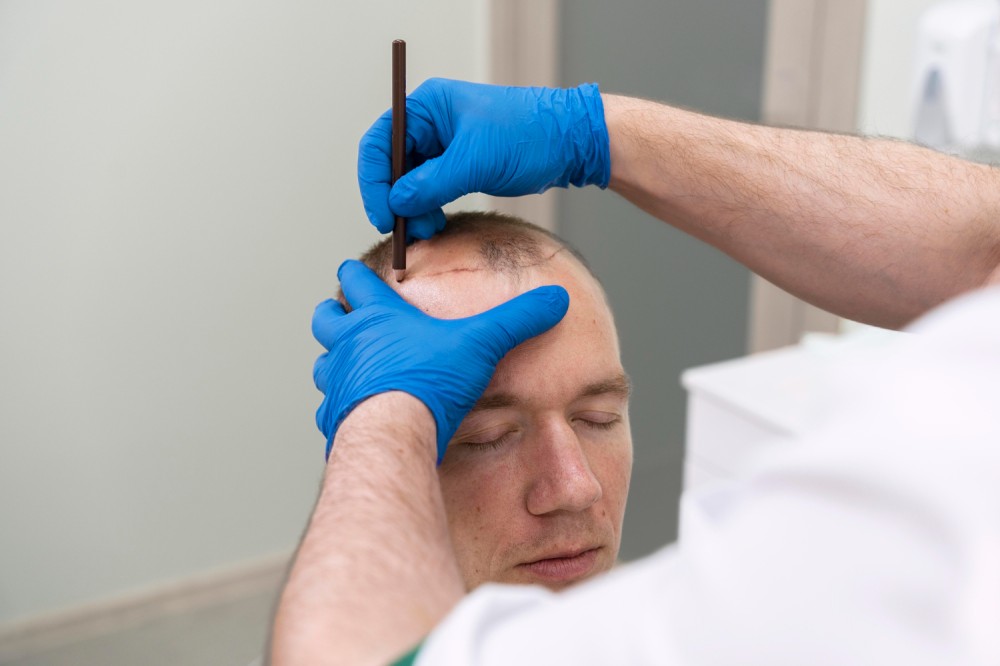
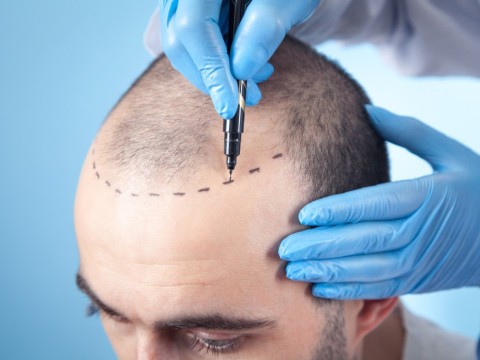
The first step before a hair transplant is examination and planning. The goal is to accurately determine the cause of hair loss and understand the patient's needs. The initial examination involves gathering information about the patient's age, chronic diseases, medications, smoking, alcohol use, allergies, and hair loss history. After investigating the patient's entire history, the doctor determines whether the patient is suitable for hair transplantation and plans the procedure, considering factors such as the number of grafts needed. This thorough examination and planning process are crucial for successful treatment.
Before the surgery, the "donor area" (where hair is taken from) is trimmed short for easy access. A local anesthetic is then injected under this area. The surgeon removes small sections of hair-bearing scalp, divides them into tiny sections, and transplants them into small holes in the scalp. Normal saline is used to minimize bleeding in the donor area. Following the existing hair direction, the surgeon creates tiny holes in the recipient area using small blades or needles. Grafts, each containing one to three hairs, are placed in these holes. After the procedure, the scalp is cleaned, covered with gauze, and a pressure bandage may be worn for a day or two.
The duration depends on the transplant size, typically taking 3 to 8 hours. Local anesthesia is used throughout the process.
Recovery varies, but most patients can resume normal activities 2 to 3 days after the procedure. Crusts from the transplant area fall off within ten days. Redness and itching in the initial stage disappear quickly. The entire process, from transplant to full results, takes 3-4 months, sometimes up to a year.
The procedure uses local anesthesia, and sometimes sedation. During surgery, you won't feel any pain. Afterward, minimal pain for a few days can be managed with painkillers.
You can have a hair transplant at any time, but there are some months and seasonal changes where you need to be extra careful during recovery for optimal results: - If you plan to have a hair transplant in the summer, protect your head from UV lights and avoid direct sunlight for at least 10 days. Post-surgery, it's recommended to skip swimming for at least 15 days.
After a hair transplant, whether FUT or FUE, both the transplanted and existing hairs may temporarily shed about three weeks post-op. This is known as "effluvium" or "shock loss." While it may be unsettling to see hair fall out, it's a temporary phase that indicates progress. After shedding, follicles lie dormant for three to eight months before new growth.
The donor area has a limited number of genetically resistant hairs, and ongoing hair loss may require additional transplants. Hair restoration surgery doesn't halt hair loss progression, even though transplanted hair is permanent.
An FUE hair transplant is effective and leaves minimal, unnoticeable scarring once the transplanted hair grows back. Recovery time is typically shorter compared to other hair surgery methods, around 10-14 days.
FUE hair transplants boast a high success rate, ranging from 95% to 100%.
FUE, or Follicular Unit Extraction, is a method of harvesting hair follicles from the donor area.
Hair transplant surgery is a permanent solution for people experiencing pattern baldness or hair loss. It is also known as hair restoration, hair grafting, hair replacement, hair surgery, or hair implants.
People who may think about getting a hair transplant include: - Those with male or female pattern baldness. - Individuals facing hair loss due to head scarring, scalp injuries, or cosmetic surgery. - People needing revision hair transplantation. - Anyone who believes they will feel better after having a hair transplant.
The best candidates for hair transplant are typically in their late 20s or older. An ideal candidate should have enough healthy donor hair on the back and sides of the head. Hair transplant is not recommended for patients younger than 25 due to unrealistic expectations in younger individuals. While hair transplantation is a minor surgery, there are still risks involved, and being in good health is crucial. If you are free from health problems like diabetes, blood pressure issues, heart, liver, and kidney failure, you may be a suitable candidate.
After the transplant, you are discharged and transferred to your hotel. The next day, a checkup and dressing are done. On the 3rd day, you return to the hospital for the first hair wash and instructions. You stay 4 days and 3 nights before being transferred to the airport.
A hair transplant is a permanent solution that can last a lifetime if the hair graft is taken from the safe zone. Protecting your existing hair from further loss may eliminate the need for additional sessions.
Transplanted hair is permanent and can be treated like natural hair, including washing, cutting, and dyeing.
Hair transplant may not be recommended if there are insufficient hair follicles on the nape, if hair is too thin, or if the patient has chronic telogen effluvium or alopecia areata.